Understanding Private Keys: Your Access to Digital Assets

In the world of cryptocurrencies, private keys are the cornerstone of security and ownership.
As of July 2025, with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) gaining mainstream adoption, understanding private keys is essential for anyone engaging with digital assets.
A private key is the cryptographic secret that grants access to your funds on a blockchain, making it both a powerful tool and a critical responsibility.
This article explains what private keys are, how they work, their role in cryptocurrency wallets, associated risks, and best practices for keeping them secure.
What Is a Private Key?
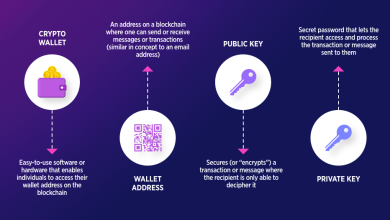
A private key is a randomly generated, secret string of numbers and letters used in cryptographic systems to prove ownership of digital assets.
In the context of cryptocurrencies, it is a unique code that allows you to sign transactions, authorizing the transfer of funds from your wallet to another address on the blockchain.
Think of it as the ultimate password: without it, you cannot access or spend your cryptocurrency, and if someone else obtains it, they can control your funds.
Private keys are paired with public keys, which are derived from them using cryptographic algorithms (e.g., Elliptic Curve Cryptography for Bitcoin and Ethereum).
While public keys generate wallet addresses that can be shared to receive funds, private keys must remain confidential.
Example
A private key might look like this (simplified for illustration):
5Kb8kLf9zgWQnogidDA76MzPL6TsZZY36hWXMssSzNydYXYB9KF
It is a long, complex string designed to be nearly impossible to guess or crack.
How Private Keys Work
Private keys are integral to the operation of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of their role:
-
Key Generation: When you create a crypto wallet (e.g., MetaMask, Ledger), it generates a private-public key pair. The private key is stored securely within the wallet, while the public key creates a wallet address for receiving funds.
-
Signing Transactions: To send cryptocurrency, you initiate a transaction in your wallet, specifying the recipient’s address and amount. The wallet uses your private key to create a digital signature, proving you own the funds.
-
Broadcasting to the Blockchain: The signed transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network, where nodes verify the signature using your public key. This ensures the transaction is legitimate without revealing the private key.
-
Access Control: The private key is the only way to access and spend the funds associated with your wallet address. Losing it means losing access to your assets, and exposing it risks theft.
-
Seed Phrase Backup: Most wallets generate a seed phrase (12–24 words) during setup, which can regenerate the private key if lost. This acts as a backup but must also be kept secret.
The Role of Private Keys in Crypto Wallets
Crypto wallets, whether hot (online, e.g., Trust Wallet) or cold (offline, e.g., Ledger Nano X), rely on private keys to manage digital assets. There are two main wallet types:
-
Non-Custodial Wallets: You control the private key (e.g., MetaMask, hardware wallets). These offer full ownership but require you to secure the key.
-
Custodial Wallets: A third party (e.g., Coinbase, Binance) holds the private key on your behalf. This is more convenient but reduces control and exposes you to risks if the provider is hacked or fails.
In non-custodial wallets, the private key is stored on your device or hardware, while custodial wallets manage it on their servers, similar to a bank holding your funds.
Why Private Keys Are Critical
Private keys are the foundation of cryptocurrency’s decentralized ethos, enabling users to control their assets without intermediaries. Their importance stems from:
-
Ownership: They prove you own the funds tied to your wallet address.
-
Security: Cryptographic strength makes private keys nearly impossible to crack with current technology.
-
Irreplaceability: Unlike traditional bank accounts, there’s no “reset password” option. Losing a private key means permanent loss of access to your assets.
-
Financial Sovereignty: Private keys empower users to manage funds independently, aligning with the crypto principle of “be your own bank.”
Risks Associated with Private Keys
-
Loss: Forgetting or losing a private key (or seed phrase) results in irreversible loss of funds, as blockchains have no central authority to recover access.
-
Theft: Hackers can steal private keys through phishing, malware, or compromised devices, gaining full control over your assets.
-
Human Error: Writing down a key incorrectly or storing it insecurely (e.g., in a digital file) increases risks.
-
Custodial Risks: In custodial wallets, you rely on the provider’s security, which may be vulnerable to hacks (e.g., Mt. Gox in 2014 lost 850,000 BTC).
-
Physical Damage: For cold wallets, physical loss or damage to a hardware device (without a seed phrase backup) can lock you out of your funds.
Best Practices for Securing Private Keys
To protect your private keys and ensure the safety of your digital assets, follow these best practices:
-
Never Share Your Private Key or Seed Phrase: Treat them like a bank PIN. Do not share them with anyone, including friends, family, or support teams claiming to “help.”
-
Store Offline: Write down your private key or seed phrase on paper or engrave it on a metal plate and store it in a secure location, such as a safe or bank vault. Avoid digital storage (e.g., screenshots, cloud drives).
-
Use Hardware Wallets: For significant holdings, use cold wallets like Ledger Nano X or Trezor, which keep private keys offline and are resistant to online attacks.
-
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For hot wallets and exchange accounts, use 2FA (preferably authenticator apps, not SMS) to add an extra layer of security.
-
Verify Platforms: Download wallets from official sources and double-check URLs to avoid phishing scams or fake apps.
-
Create Multiple Backups: Store seed phrase copies in separate, secure locations (e.g., a safe at home and a bank vault). Ensure they are protected from fire, water, or theft.
-
Test Recovery: Periodically verify your seed phrase by testing wallet recovery on a secure device to ensure it works.
-
Beware of Phishing: Avoid clicking suspicious links or entering private keys on unverified websites. Scammers often pose as wallet providers or exchanges.
-
Update Software: Keep wallet software and devices updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
-
Use Multi-Signature Wallets: For advanced users, multi-signature wallets require multiple private keys to authorize transactions, reducing the risk of single-key compromise.
Private Keys in 2025
As of July 2025, the importance of private keys remains central to the crypto ecosystem. With Bitcoin trading between $50,000 and $80,000 and Ethereum targeting $4,000–$6,000, the value of digital assets underscores the need for robust security.
Non-custodial wallets like MetaMask and Trust Wallet are popular for interacting with DeFi and NFTs, while hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor dominate for secure storage.
The rise of custodial wallets on exchanges like Coinbase reflects growing mainstream adoption, but high-profile hacks emphasize the risks of relinquishing private key control. Innovations like multi-signature wallets and advanced encryption are enhancing security, but user education remains critical.
Getting Started with Private Keys
For beginners:
-
Choose a Wallet: Start with a reputable non-custodial wallet (e.g., MetaMask for hot, Ledger for cold) to maintain control of your private key.
-
Set Up Securely: During wallet creation, carefully record the seed phrase and store it offline. Never save it digitally.
-
Test Small Amounts: Transfer a small amount of crypto to your wallet to practice sending and receiving, ensuring you understand key management.
-
Learn More: Read resources like Mastering Bitcoin by Andreas Antonopoulos or Binance Academy articles on wallet security.
-
Stay Vigilant: Monitor X and other platforms for scam alerts and follow trusted crypto communities for updates.